Component of concerete
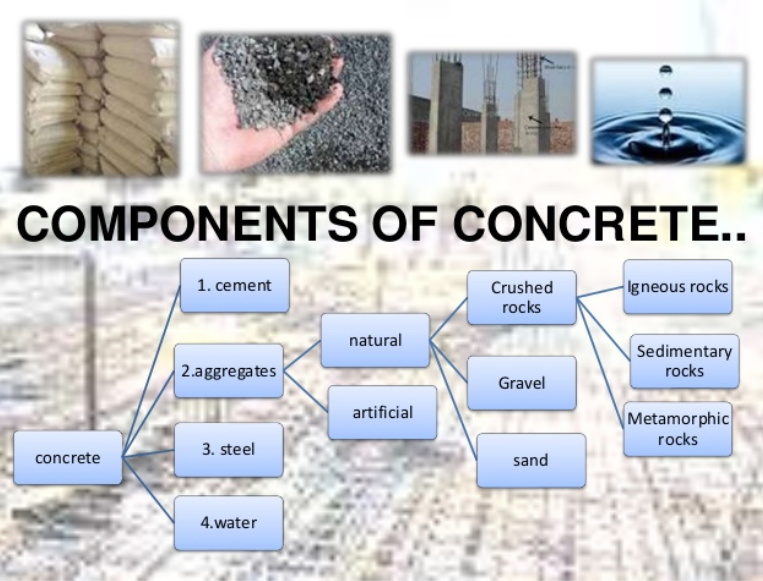
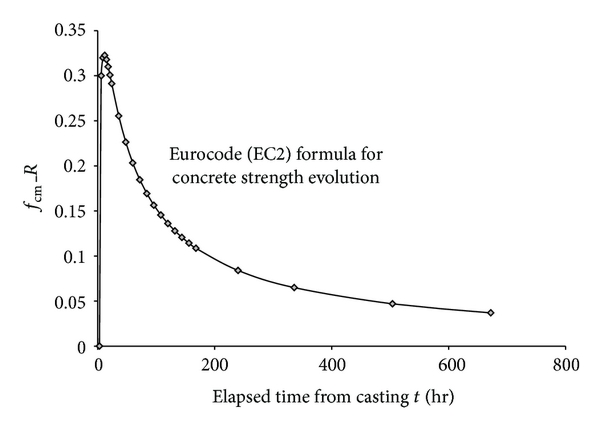
Concrete is a mix of cement, fine aggregate (sand), coarse aggregate (gravel or crushed stone), and water. Concrete is the most widely used construction material in the world. Concretes are similar in composition to mortars which are used to bond unit masonry. Mortars, however, are normally made with sand as the sole aggregate, whereas concretes contain both fine aggregates and much larger size aggregates and thus usually have greater strength. Concretes therefore have a much wider range of structural applications, including pavements, footings, pipes, unit masonry, floor slabs, beams, columns, walls, dams, and tanks. There are many different types of concrete.
Important properties of concrete, governing design of a concrete mix, are strength, durability, workability, economy. Durability of concrete means capability of concrete to resist its disintegration and decay. Workability is a measure of the ease with which a fresh mix of concrete or mortar can be mixed, subsequently handled, transported, placed, finished with a minimum loss of homogeneity and without bleeding or segregation in the finished product. It depends on water in the mix, ratio of coarse and fine aggregates, particle interference and interlocking etc. Mixing of concrete can be done by hand mixing or machine mixing. Concrete should be thoroughly compacted during the operation of placing and should be properly placed around reinforcement. Concrete may be compacted manually by rodding, tamping, and sometimes Internal or immersion vibtator, external or form vibrator, surface vibrator can be used for compaction purpose. Concrete should be properly cured for gaining its strength and hardness.
In good concrete the ingredients must be of right proportioned, cohesive enough to be transported, placed in such a way that ingredients must not segregated from each other. Moreover the good concrete must be workable and can be compacted. In mixing of fresh concrete and in curing of hardened concrete water is necessary. Potable water, fit for human consumption, is generally considered to be suitable for concreting. Concrete must be workable in fresh state, and must have impermeability and durability in hardened state.
Grade of concrete is represented in terms of a number preceded by the letter ‘M’. M refers to “mix” viz. aggregate, sand, cement. And The number denotes characteristic compressive strength of 150mm cubes at 28 days in MPa(N/mm^2).The “mix” for a specified grade involves the economical selection of relative proportion of cement, fine aggregate, coarse aggregate and water(admixture, if any).
To modify property of concrete some chemical & mineral admixture are used. Chemical admixtures are – retarders(such as sugar and other chemicals are used in hot weather concreting and in ready-mixed concreting),accelerators(such as calcium chloride ,used in cold weather ) water-reducers,superplasticizers,air-entraining agents(such as animal/vegetable fats & oils),bonding admixtures . Mineral admixtures i.e. very fine-grained inorganic materials having pozzolanic or latent hydraulic properties are added to the concrete mix to improve the properties of concrete. Some mineral admixtures are Fly ash, Silica fume, Ground granulated blast furnace slag (GGBFS or GGBS), High reactivity Metakaolin (HRM) etc
Source: https://www.livewebtutors.com/assignment-help/civil-engineering/concrete